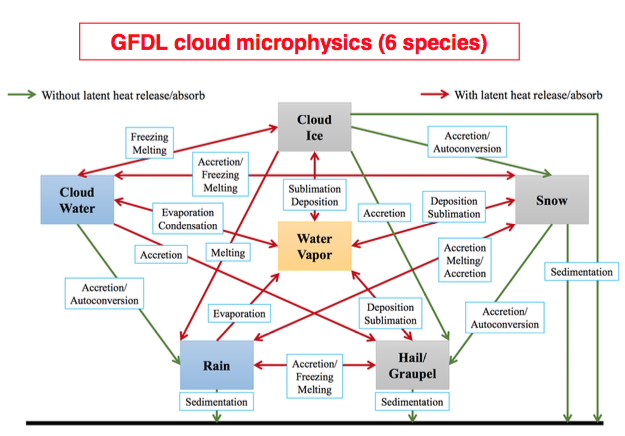
GFDL cloud microphysics (MP) scheme is a six-category MP scheme to replace Zhao-Carr MP scheme, and moves the GFS from a total cloud water variable to five predicted hydrometeors (cloud water, cloud ice, rain, snow and graupel). This scheme utilizes the "bulk water" microphysical parameterization technique in Lin et al. (1983) [120] and has been significantly improved over years at GFDL (Lord et al. (1984) [126], Krueger et al. (1995) [114], Chen and Lin (2011) [36], Chen and Lin (2013) [37]). Physics processes of GFDL cloud MP are described in Figure 1 (also see warm_rain() and icloud()) and are feature with time-split between warm-rain (faster) and ice-phase (slower) processes (see 'conversion time scale' in gfdl_cloud_microphys.F90 for default values).
Some unique attributes of GFDL cloud microphysics include:
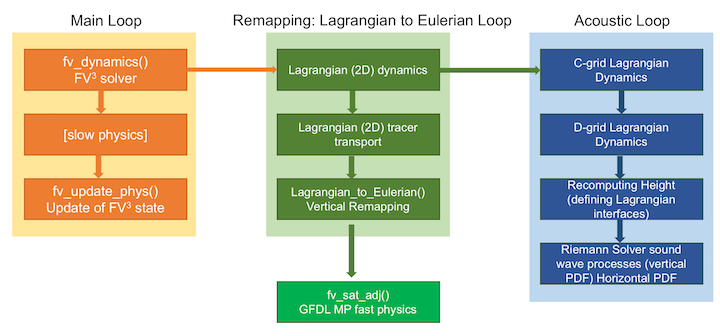
The leftmost column of Figure 1 shows the external API calls used during a typical process-split model integration procedure. First, the solver is called, which advances the solver a full "physics" time step. This updated state is then passed to the physical parameterization package, which then computes the physics tendencies over the same time interval. Finally, the tendencies are then used to update the model state using a forward-in-time evaluation consistent with the dynamics.
There are two levels of time-stepping inside FV3. The first is the "remapping" loop, the green column in Figure 1. This loop has three steps:
This loop is typically performed once per call to the solver, although it is possible to improve the model's stability by executing the loop (and thereby the vertical remapping) multiple times per solver call.
At grid spacing of less than ~10 km, model dynamics should be able to "see" and "feel" the cloud and precipitation condensate; heat content, heat exchange with the environment, and momentum of condensate should be accounted for. The GFDL microphysics scheme is formulated to accomplish this through strict moist energy conservation during phase changes, and keeping heat and momentum budgets for all condensate. This results in thermodynamic consistency between the FV3 microphysics scheme and FV3 dyanmics.
In current fv3gfs, GFDL in-core fast saturation adjustment (phase-changes only) is called after the "Lagrangian-to-Eulerain" remapping. When GFDL In-Core Fast Saturation Adjustment Module is activated (do_sat_adj=.true. in fv_core_nml block), it adjusts cloud water evaporation (cloud water \(\rightarrow\)water vapor), cloud water freezing (cloud water \(\rightarrow\)cloud ice), and cloud ice deposition (water vapor \(\rightarrow\)cloud ice). The process of condensation is an interesting and well known example. Say dynamics lifts a column of air above saturation, then an adjustment is made to temperature and moisture in order to reach saturation. The tendency of the dynamics has been included in this procedure in order to have the correct balance.
Scale-awareness provided by assumed subgrid variability that is directly proportional to grid spacing. Horizontal sub-grid variability is a function of cell area:
\[ h_{var}=\min \left\{0.2,\max\left[0.01, D_{land}(\frac{A_{r}}{10^{10}})^{0.25}\right]\right\} \]
\[ h_{var}=\min \left\{0.2,\max\left[0.01, D_{ocean}(\frac{A_{r}}{10^{10}})^{0.25}\right]\right\} \]
Where \(A_{r}\) is cell area, \(D_{land}\) and \(D_{ocean}\) are base values for sub-grid variability over land and ocean (larger sub-grid variability appears in larger area). Horizontal sub-grid variability is used in cloud fraction, relative humidity calculation, evaporation and condensation processes. Scale-awareness is achieved by this horizontal subgrid variability and a \(2^{nd}\) order FV-type vertical reconstruction (Lin et al. (1994) [121]).